Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Naked nuclei (NN) are observed upon examining bone marrow aspirate slides from healthy individuals and from those with hematologic malignancies, but are not well understood. Without characteristic findings like cytoplasm or plasma membrane, NN are considered remnants of slide preparation or are discounted as cells of undetermined significance. NN have been associated with poor prognosis in several solid cancers. Understanding the significance of NN in hematologic malignancies such as acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) may elucidate valuable diagnostic and prognostic knowledge. Decellularized Wharton's jelly matrix (DWJM) is an extra cellular matrix (ECM)-based in vitro model that shares similar elements with the bone marrow ECM and can be used as scaffolding to culture leukemia cells. We hypothesize that NN exist in AML and interact with other cells, suggesting potential biological relevance within the bone marrow microenvironment.
METHODS
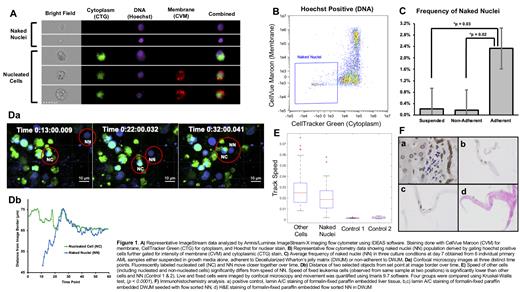
Primary AML samples obtained by leukapheresis were cultured in suspension with growth media or in the presence of DWJM submerged in growth media. In samples grown with DWJM, cells that were non-adherent to the matrix were collected first and then adherent cells were isolated by treating DWJM with collagenase. Live cells were stained with CellVue Maroon (CVM) for membrane, CellTracker Green (CTG) for cytoplasm, and Hoechst 33342 for nucleus, followed by analysis with Amnis/Luminex ImageStream-X imaging flow cytometer (Figure 1A). NN were defined as events positive for nuclear stain and negative for cytoplasmic and membrane stains (Figure 1B). 3-D movement of adherent AML cells in DWJM was captured in real time using confocal microscopy. Fixed cells from leukemia cell line K562 served as a control for movement. NN (Hoechst positive only), non-nucleated (Hoechst negative/CTG positive), and nucleated cells (Hoechst and CTG positive) were identified by fluorescent labeling. NN were also observed after isolation by cell sorting. Cell speed, cell displacement from origin, and change in distance to closest neighboring cell over time were measured. Additionally, flow sorted NN were examined by immunohistochemistry (IHC).
RESULTS
Adherent populations contained significantly more NN than non-adherent and suspension populations. The frequency of NN in matrix adherent cells ranged from 0.4-2.4% at day 3 and 0.5-5.4% at day 7 of culture (Figure 1C). Through confocal microscopic analysis, we observed NN, nucleated, and non-nucleated cells moving at speeds ranging from 0.002-0.08 µm/sec. Fixed cells showed no discernible movement in DWJM. The average speed of NN [0.019 mm/s, SD 0.011] significantly differed from the average speed of nucleated and non-nucleated cells [0.027 mm/s, SD 0.016] (p=0.004) (Figure 1E). To demonstrate directional movement, we measured change in distance between NN and closest neighboring nucleated or non-nucleated cells over time. Cells (nucleated and non-nucleated) and NN moved closer to each other over time suggesting directional movement (p=0.001) (Figure 1D). NN also showed movement in DWJM after isolation by cell sorting. IHC analysis showed sorted NN stained positive for nuclear lamin A/C, which are considered markers of nuclear membrane (Figure 1F).
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings confirm that NN are present in primary AML cells cultured in vitro using ourECM-based model and that they can be isolated using flow cytometry. Additionally, NN display directional movement in DWJM suggesting that they interact with other cells and may be biologically relevant structures in the bone marrow microenvironment.
Baran: AstraZeneca/Acerta: Research Funding. Chu: Pfizer: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Acerta/AstraZeneca: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal